Batteries, cells
| Datasheet: | Download |
Batteries Ni-Cd (nickel-cadmium), Ni-MH (nickel-metal hydride), Li-Ion (lithium-ion) and LiFePO4 (lithium-iron-phosphate) are used to supply emergency lighting power supply.
As standard, the battery leads are 20 cm outside the battery outline and are terminated with a N-type connector, adapted to the plug mounted in HYBRYD emergency power supply systems.
FEATURES
• Suitable for use in high temperature (-5° – +60°C)
• Selected packages are also available in thermostated version, which allows them to be used at reduced temperatures (from -20°C)
• Many ways of packing
• High current efficiency
• Low self-discharge
• Long life
• No memory effect (Li-Ion, LiFePO4)
• Fast charging process
OPERATING CONDITIONS
| Ni-Cd | Ni-MH | Li-Ion | LiFePO4 | |
| Cell temperature during charging | 0°C – +55°C | 0°C – +55°C | 0°C – +60°C | 0°C – +60°C |
| Cell temperature during operation | -5° – +60°C | -5° – +60°C | -20° – +60°C | -20° – +60°C |
Ni-Cd and Ni-MH battery obtain full electrical parameters after three complete charge and discharge cycles.
With the fulfillment of proper operating conditions, battery capacity measured by a 0.1C discharge current should not fall below 60% of its rated capacity within a period of 48 months from the date of manufacture.
The number of charge / discharge cycles during this time period should not exceed 300.
The battery-powered system controls the battery voltage cut-off to protect against deep discharge.
BATTERY VOLTAGE AND CAPACITY
The batteries are made up of individual battery cells connected in series (L). Single cell voltage (N) is 1,2V (for Ni-Cd, Ni-MH), 3,7V (for Li-Ion) and 3,2V (for LiFePO4). The battery voltage is: L x N.
Depending on the type and power of the lighting source and the required lighting efficiency, HYBRYD emergency power supply systems are powered by a battery consisting of 2, 3,
4, 5 and 7 cells.
The battery capacity depends on the execution of the system’s current and the required emergency operation time.
The mostly used capacities are shown in the table below:
| Ni-Cd | Ni-MH | Li-Ion | LiFePO4 |
| 1,5Ah | 1,6Ah | 0,7Ah | 0,6Ah |
| 2,5Ah | 2,1Ah | 2,2Ah | 1,5Ah |
| 4,0Ah | 4,0Ah | 2,0Ah |
PACKING TYPE – MOUNTING
As standard, the batteries are packing in series or in parallel. If a different way of battery cells packing is required, it is recommended to contact HYBRYD.
Ni-Cd batteries of PAR and PAS type are mounted using clamps or cable ties. Ni-MH batteries of PAR, PAS, PAP, PAK, PAC, PAD type are mounted using cable ties.
The most commonly used types of packing:
PAO type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 3,6-8,4V) battery packed in series, can be equipped with clamps

PAS type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 3,6-8,4V) battery packed in series, without clamp
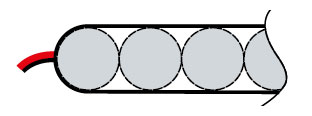
PAP type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 3,6V) 2 cells located in parallel and the third placed on them
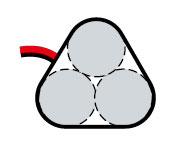
PAK type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 6,0V) 3 cells located in parallel and two placed on them
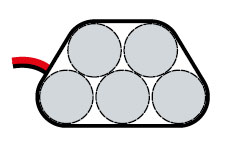
PAC type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 4,8V) 4 cells arranged in a cuboid
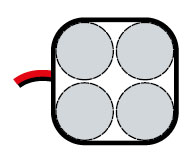
PAD type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 8,4V) double cuboid, arranged with 7 cells
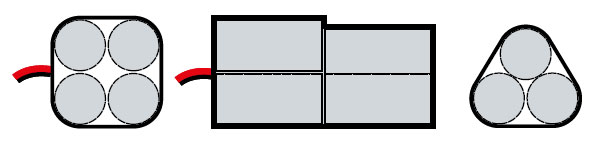

PAE type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 7,2V)

PAL type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 4,8V; 7,2V)
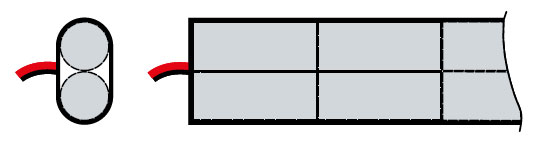
PAT type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 12,0V)
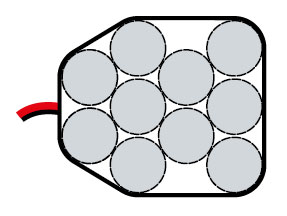
PAB type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 3,6V; 6,0V; 8,4V)
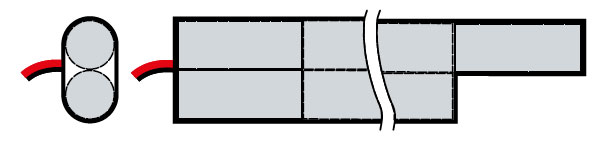
PAN type – (Ni-Cd, Ni-MH; 3,6V; 6,0V; 8,4V)
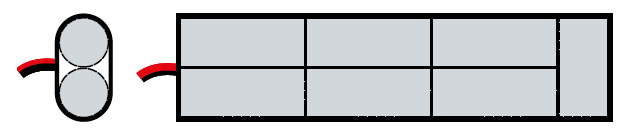
PAW type – (Ni-MH; 4,8V)

 MENU
MENU